STORM-PE
Randomized Controlled Trial
First-of-its-kind RCT for acute intermediate-high
risk pulmonary embolism (PE).
CAVT™ – Now Proven by Level 1 Evidencec


Prospective, Randomized Trial
Acute, Intermediate-High Risk PE
22 International Sites

100 Participants
-
Evaluate the efficacy and assess safety of treating acute, intermediate-high risk pulmonary embolism with anticoagulation alone versus anticoagulation plus computer assisted vacuum thrombectomy (CAVT) with the Indigo® Aspiration System.
-
- Change in RV/LV ratio assessed by CTPA at 48-hoursa
- Major adverse events within 7 daysb
- Safety (symptomatic PE recurrence, all-cause mortality and PE-related mortality) as well as functional outcomes and quality of life assessments at 90 days
a. Results adjudicated by a blinded, independent imaging Core Lab
b. Major adverse event is defined as a composite of clinical deterioration requiring escalation of care, PE-related mortality, symptomatic recurrent PE, or major bleeding. -
STORM-PE patients were randomized 1:1, divided into the computer assisted vacuum thrombectomy (CAVT) plus anticoagulation arm or the anticoagulation alone arm.
-
- Symptom onset of 14 days or less
- Acute PE with proximal filling defect confirmed by CTPA
- Intermediate-high risk PE demonstrated by RV/LV ratio and elevated biomarkers
Results Now Published in American Heart Association Journal: Circulation
Trial Design Manuscript Published in American Heart Journal
ClinicalTrials.gov Study Site
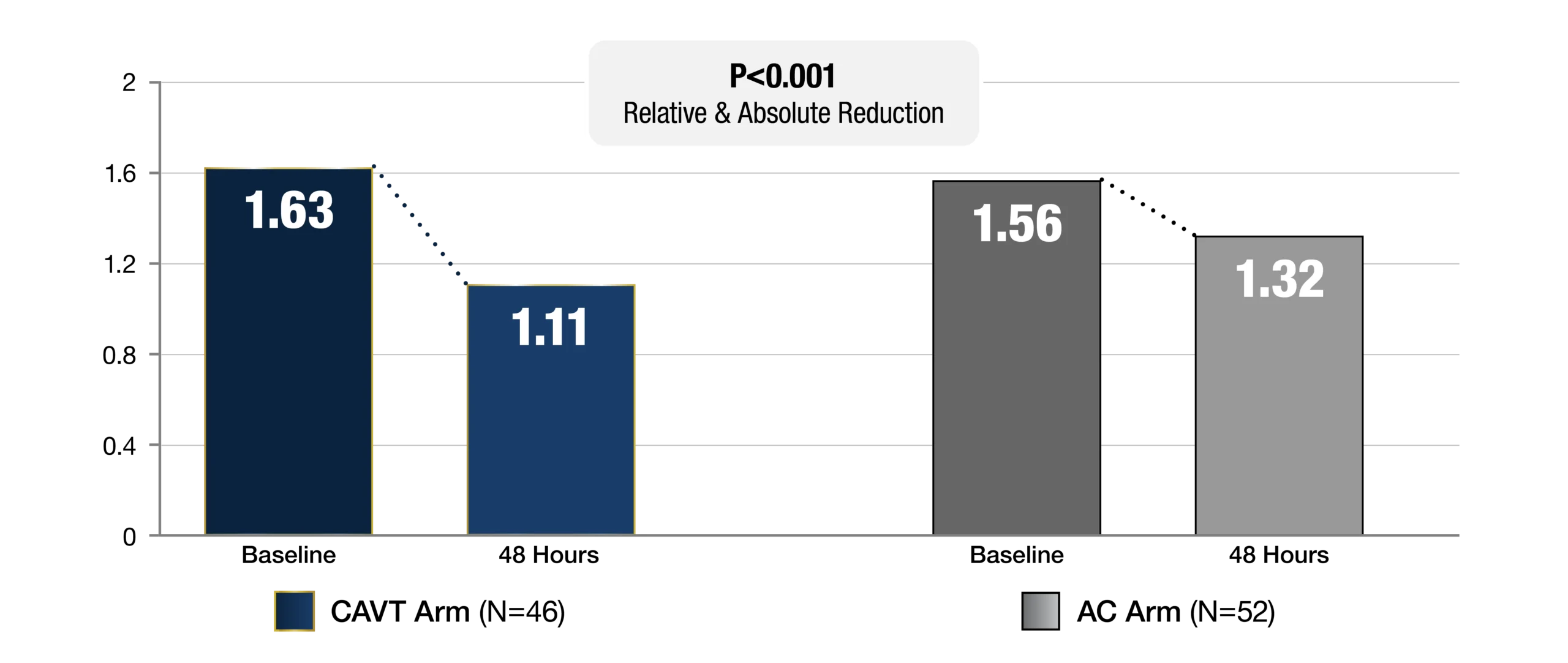
Primary Endpoint
RV/LV Reduction Baseline to 48 Hours

Expanded RV/LV Analysis
48 Hour RV/LV Reduction > 0.2

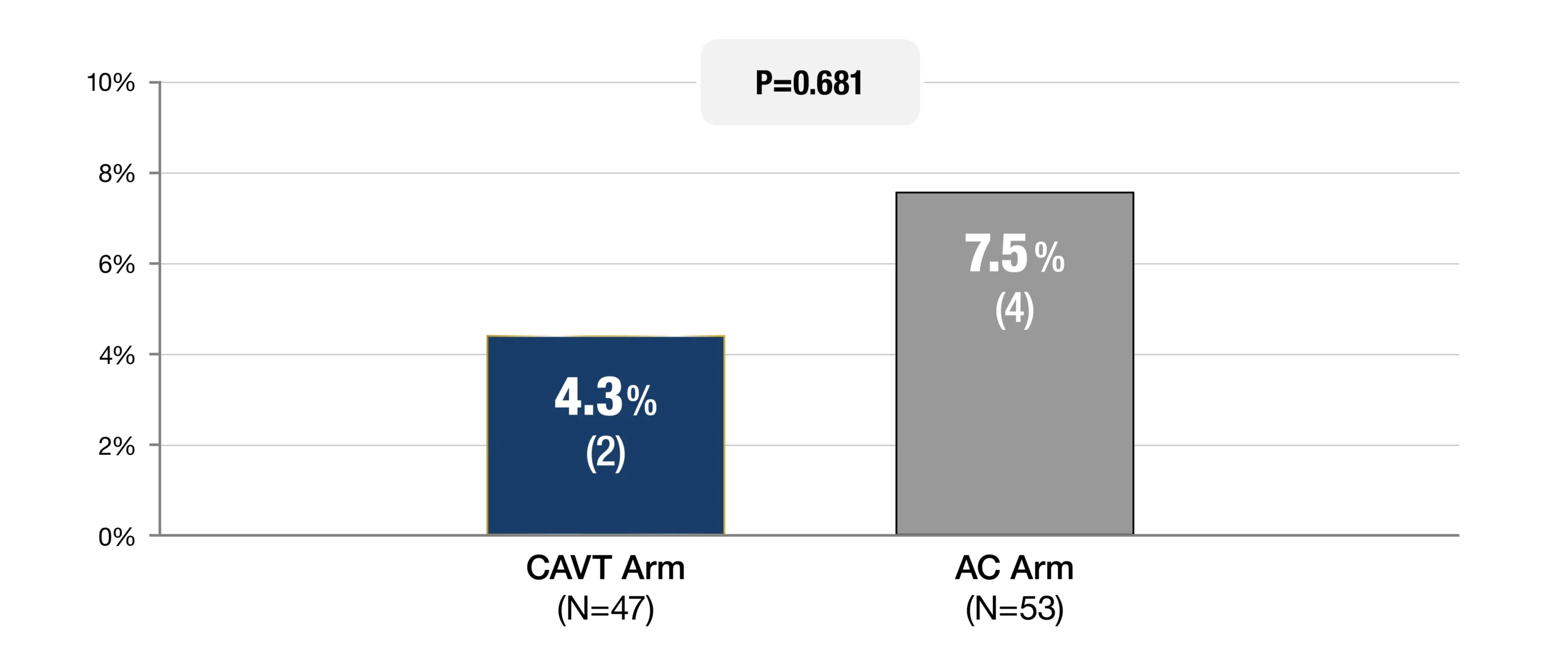
Safety Endpoint
-
Composite MAE ≤ 7 Days (%, n)
-
Major Bleeding (BARC 3a-5)e

Clinical Outcomes
-
Tachycardia HR > 100 bpm, % of Patients

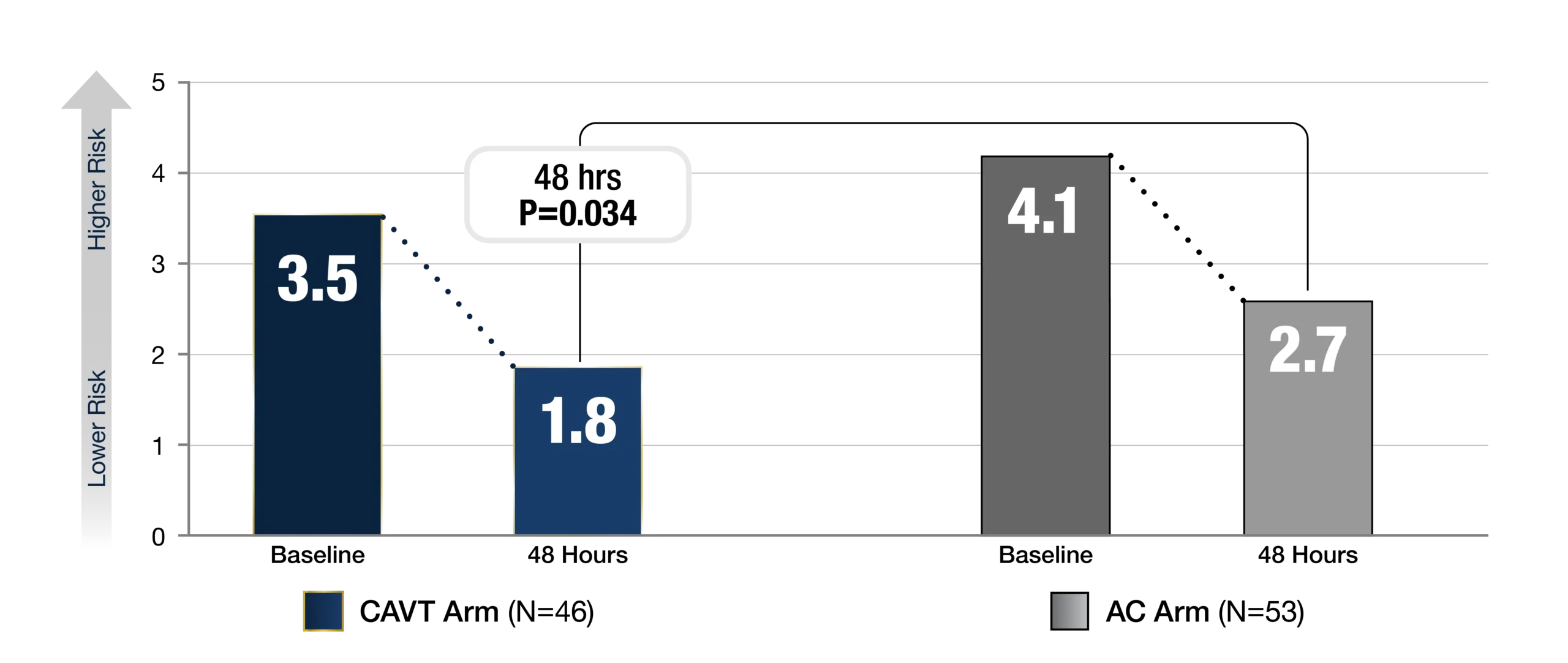
-
NEWS2 Score at Baseline & 48 Hours
Functional Endpoint
% of predicted 6 Minute Walk Distance (6MWD) at 90 days

Procedure Data
-
Device Time (median)
25 min
[15.0, 41.0]
-
Procedure Time (median)
56 min
[42.0, 69.0]
-
mPAP Reduction (mean)
27.3%
(8.2 mmHg)
-
Technical
Successh100%
(47/47)
-
Device Related Transfusion
0%
(0/47)
National Principal Investigators
Massachusetts General Hospital Rachel Rosovsky, MD
Hematology
Mount Sinai Hospital Robert Lookstein, MD
Interventional Radiology
Steering Committee Members
Massachusetts General Brigham Ido Weinberg, MD
Vascular Medicine
UCLA Medical Center Richard Channick, MD
Pulmonology
UCLA Medical Center John Moriarty, MD
Interventional Radiology
Columbia University Medical Center Sahil Parikh, MD
Interventional Cardiology
University Medical Center Mainz Stavros Konstantinides, MD
Cardiology
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Suhail Dohad, MD
Interventional Cardiology
Richard Davis
Patient Representative
c. Lookstein, R. A., Konstantinides, S. V., Weinberg, I., Dohad, S. Y., Rosol, Z., Kopeć, G., Moriarty, J. M., Parikh, S. A., Holden, A., Channick, R. N., McDonald, B., Nagarsheth, K. H., Yamada, K., & Rosovsky, R. P. (2025). Randomized controlled trial of mechanical thrombectomy with anticoagulation versus anticoagulation alone for acute intermediate-high risk pulmonary embolism: Primary outcomes from the STORM-PE trial. Circulation. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.125.077232
d. STORM-PE was not powered to detect differences in safety
e. Type 3a was not considered major bleeding if it was related to an expected decrease in hemoglobin level due to fluid administration and if transfusion was less than 2 units
f. Timepoint closest to randomization, after administration of AC and pre-procedure for the CAVT arm. Paired data represented.
g. Enright, PL, & Sherrill, DL. Reference equations for the six-minute walk in healthy adults. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;158(5 Pt 1):1384–1387
h. Ability of catheter to access clot and perform aspiration
STORM-PE demonstrated superiority to anticoagulation utilizing Lightning Flash® 1.0 and 2.0. Efficacy was predefined as the difference between treatment arms in change of RV/LV ratio from baseline to 48 hrs. The clinical results presented herein are for informational purposes only, and may not be predictive for all patients. Individual results may vary based on patient specific-attributes and other factors
